
Mastering Power Query In Excel: Step By Step Guide
Power Query in Excel, also known as Get & Transform Data in Microsoft Excel, is a powerful built-in tool (available natively in Excel 2016 and later, including Microsoft 365) that revolutionizes data management for users of all levels.
It enables seamless importing and connecting to data from diverse sources—such as Excel files, CSV, databases, web pages, APIs, and cloud services—without requiring complex coding.
Once connected, Power Query’s intuitive editor allows users to clean, transform, and reshape data effortlessly: remove duplicates, filter rows, split or merge columns, change data types, unpivot tables, add conditional logic, and combine multiple datasets.
These steps are recorded automatically, making processes repeatable and refreshable with a single click, ensuring reports stay up-to-date as source data changes.
Table of Contents
- What Is Power Query In Excel?
- Importance Of Power Query In Excel
- Ways To Import Data With Power Query
- Transforming Data Using Power Query
- Step By Step Process
- Power Query Editor
- Main Components Of Power Query Editor
- Advanced Power Query Techniques
- Best Practices For Using The Power Query Editor
- FAQ(Frequently Asked Questions)
- Final Takeaway
What Is Power Query In Excel?
Power Query is a powerful data connection and transformation tool built into Microsoft Excel (available as Get & Transform Data in Excel 2016 and later, including Microsoft 365).
It allows users to easily discover, connect to, and import data from a wide variety of sources—such as Excel workbooks, CSV files, databases, websites, APIs, folders, and cloud services like SharePoint or Azure.
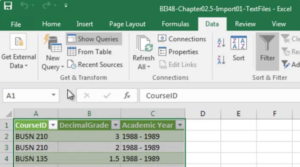
Importance Of Power Query In Excel
The Importance of Power Query in Excel is huge and it is one of the most transformative tools in modern Excel, especially for anyone dealing with data regularly—analysts, accountants, finance professionals, and business users.
1. Saves Massive Time On Data Preparation
Data cleaning and transformation often take 80% of analysis time. Power Query automates repetitive tasks like removing duplicates, filtering, splitting columns, handling missing values, and reshaping data—with just a few clicks.
2. Connect To Almost Any Data Source
Import data seamlessly from Excel files, CSV, databases (SQL, Access), web pages, APIs, folders, SharePoint, and cloud services—no more copy-pasting or manual imports. However, you need to make your choices in the correct order to make the right use of power query in Excel.
3. Makes The Process Repeatable & Refreshable
Every step is recorded. When source data updates, simply click Refresh to re-run the entire transformation automatically—perfect for monthly reports or dashboards. Ensure that you follow the correct process from your end. The correct application of power query in Excel can help you to complete your data recording task easy and recordable.
4. Ensures Data Accuracy & Consistency
Reduces human errors from manual editing. Transformations are rule-based and auditable via the Applied Steps pane.
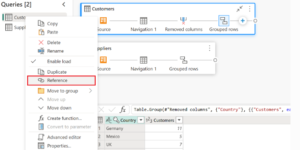
5. Empowers Non Technical Users
Its intuitive interface requires no coding (though advanced users can edit M code), democratizing powerful ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) capabilities. This is one of the crucial aspects of power Query in Excel.
6. Prepares Data Perfectly For Analysis
Clean, structured output loads directly into PivotTables, charts, or Power Pivot for advanced modeling and reporting. Power query in excel will help you to maintain the accuracy in your record keeping process with complete precision.

Ways To Import Data With Power Query
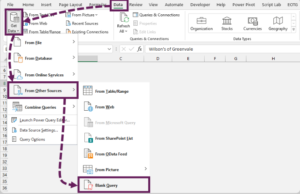
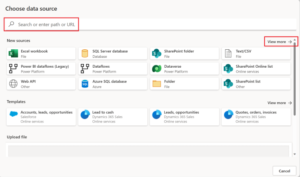
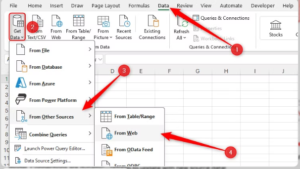
Power Query provides numerous flexible ways to import data into Excel. Start by going to the Data tab > Get Data (or Get & Transform Data group). This opens a dropdown menu with categories like From File, From Database, From Online Services, and more.
1. From File
- Excel Workbook: Import tables or sheets from another Excel file (or even the current workbook).
- Text/CSV: Load delimited files quickly.
- XML or JSON: Parse structured data files.
- PDF: Extract tables from PDF documents (great for reports).
- From Folder: Combine multiple similar files (e.g., monthly CSVs) into one table automatically—ideal for consolidating data.
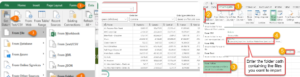
2. From Database
- Connect to SQL Server, Access, Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.
- Write custom queries or select tables/views directly. Perfect for large datasets without exporting manually.
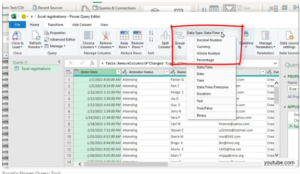
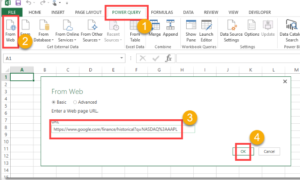
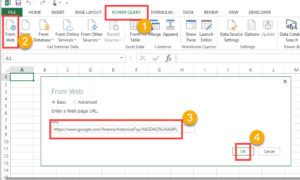
3. From Web
Enter a URL to scrape tables, lists, or navigable data from websites. Power Query detects and imports structured content easily.
4. From Online Services/ Other Sources
- SharePoint, OneDrive, Azure, Salesforce, Google Analytics, etc.
- Blank Query: Start with manual M code for advanced scenarios.
- From Table/Range: Convert existing Excel data into a query for cleaning.
Transforming Data Using Power Query
Transforming data in Power Query is straightforward and powerful. After importing data (via Data > Get Data), it opens in the Power Query Editor—a dedicated window for cleaning and reshaping.
Step By Step Process
1. Access The Editor
- Right-click a query in the Queries pane (or use Data > Get Data > Launch Power Query Editor).
2. Use The Ribbon Tabs
- Home: Common actions like Remove Rows/Columns, Sort, Filter, Merge/Append Queries, and Group By.
- Transform: Column operations (Split, Merge, Data Type changes, Replace Values, Extract Text).
- Add Column: Create custom columns, conditional columns, or from examples.
- View: Toggle Advanced Editor (for M code) or Applied Steps.
3. Apply Transformations
- Remove Duplicates: Select columns > Home > Remove Rows > Remove Duplicates.
- Split Column: Transform > Split Column > By Delimiter/Number of Characters.
- Merge Columns: Transform > Merge Columns.
- Filter/Sort: Click column headers for quick filters.
- Change Data Types: Select column > Change Type.
- Unpivot/Pivot: For reshaping wide/narrow data.
4. Monitor Applied Steps
- Every action is recorded here—click to edit/delete/reorder steps for full reproducibility.
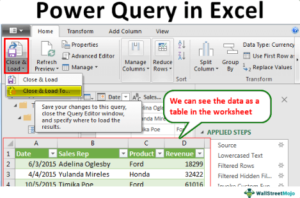
5. Finish The Process
- Click Home > Close & Load to output to Excel sheet, PivotTable, or data model. Refresh anytime for updates!
Few insightful articles on Excel to improve your knowledge:
Power Query Editor
The Power Query Editor is a dedicated graphical interface in Microsoft Excel (and Power BI) designed specifically for cleaning, transforming, and shaping data after it’s been imported using Power Query. It provides a visual, step-by-step environment where you can perform complex data manipulations without writing formulas or code.
You access it by importing data (Data > Get Data), then selecting Transform Data, or by right-clicking a query and choosing Edit.
Main Components Of Power Query Editor
1. Ribbon Tabs
Organized into sections like Home (for removing rows, sorting, merging queries), Transform (for column operations like splitting or replacing values), Add Column (for creating new calculated or conditional columns), and View (for advanced options like editing M code).
2. Queries Pane
Displays a list of all queries in your workbook. Here, you can manage, rename, group, or duplicate queries.
3. Data Preview Pane
Shows a live, interactive view of your current data table. Changes appear instantly as you apply transformations.
4. Applied Steps Pane
The most powerful feature—it automatically records every action as a sequential step. You can click any step to preview results, edit, delete, or reorder them, ensuring full transparency and easy troubleshooting.
Advanced Power Query Techniques
Advanced techniques in Power Query elevate it from basic data cleaning to a full-fledged ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool, enabling complex automation, scalability, and precision for large or intricate datasets.
-
- M Language and Advanced Editor: For ultimate control, use the Advanced Editor to view, edit, or write M code directly. This is ideal for custom logic that the GUI can’t handle easily.
- Custom Functions and Parameters: Create reusable custom functions (e.g., for repeated transformations) and parameters (e.g., dynamic file paths or dates) to make queries interactive and flexible.
- Merging and Appending Queries: Combine datasets horizontally (Merge: like SQL joins, including fuzzy matching) or vertically (Append). Supports inner/left/right joins and advanced matching.
- Fuzzy Matching: Match similar text (e.g., names with typos) during merges using tolerance settings—great for deduplication or reconciling messy data.
- Conditional and Index Columns: Add sophisticated logic with nested conditions or dynamic indexing for ranking/scenario analysis.
- Diagram View and Query Dependencies:Visualize query relationships and dependencies to manage complex models with multiple interconnected queries.
- Diagram View and Query Dependencies: Visualize query relationships and dependencies to manage complex models with multiple interconnected queries.
Best Practices For Using The Power Query Editor
Adopting best practices in Power Query ensures your data workflows are efficient, performant, maintainable, and scalable—especially for recurring reports or large datasets. These recommendations come from Microsoft guidelines and expert experiences.
- Filter and Remove Data Early: Apply row filters and remove unnecessary columns right after import. This reduces memory usage and enables query folding (where operations are pushed to the source database for faster execution).
- Maximize Query Folding: Perform folding-compatible steps (filters, sorts, some merges) early. Check the Applied Steps pane for the folding indicator to confirm operations are pushed back to the source.
- Rename and Document Thoroughly: Give meaningful names to queries, steps, and columns. Right-click steps > Properties to add descriptions—this aids collaboration and future maintenance.
- Use Staging Queries and Referencing: Create “staging” queries for raw imports and initial cleaning, then Reference them for final transformations. This keeps raw data intact and builds modular, dependency-managed models.
- Implement Parameters for Dynamic Queries: Use parameters for file paths, dates, or filters to make queries flexible and reusable without editing code.
- Set Data Types Early and Handle Errors: Change column types soon after import. Replace or remove errors proactively to avoid downstream issues.
- Organize Queries with Groups: Group related queries in the Queries pane for better navigation in complex projects.
- Test with Sample Data: During development, keep a small row sample (e.g., top 1000 rows) for faster previews, then remove before final load.
FAQ(Frequently Asked Questions)
- What is Power Query in Excel?
Power Query (also known as Get & Transform Data) is a built-in tool in Excel (2016 and later, including Microsoft 365) that allows you to discover, connect to, import, clean, and transform data from various sources without coding. It automates repetitive tasks and prepares data for analysis.
- How do I access Power Query in Excel?
Go to the Data tab on the ribbon, then click Get Data (or Get & Transform Data) to import from files, databases, web, or other sources. To edit transformations, use Transform Data to open the Power Query Editor.
- How do I refresh data in Power Query?
Once data is loaded, right-click the output table and select Refresh, or go to Data > Refresh All. Queries automatically re-run all transformation steps when the source updates.
- Is Power Query available in older versions of Excel?
It’s fully built-in from Excel 2016 onward. For Excel 2010/2013, you can download the free Power Query add-in from Microsoft, but it’s no longer updated—upgrading is recommended.
- What is the Power Query Editor used for?
It’s the main interface for transforming data: filtering rows, splitting/merging columns, removing duplicates, changing types, and more. Every step is recorded for easy editing and reproducibility.
Final Takeaway
Hence, these are some of the crucial facts about power query in Excel that you must be well aware off. For making the process of record keeping smoother. It plays a crucial part. You cannot just use this tool for upgrading your system.
You can share your views and opinions in our comment box. This will help us to know your take on this matter. Here, proper application of the software matters a lot.
- How to Delete Ledger in TallyPrime - February 11, 2026
- 3 Smart Ways to Speed Up Data Entry and Processing in Excel - January 27, 2026
- How to Convert Images Containing Tables into Editable Excel - January 27, 2026