
Guide To AI In Accounting: Trends, Tools, And Stats
AI in accounting is revolutionizing the accounting industry by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing accuracy, and enabling data-driven decision-making. AI technologies, such as machine learning, natural language processing, and robotic process automation, streamline processes like bookkeeping, auditing, and financial reporting.
By analyzing vast datasets, AI identifies patterns, detects anomalies, and predicts financial trends, improving efficiency and reducing human error. For instance, AI-powered tools can automate invoice processing, expense tracking, and tax compliance, saving time and costs.
Additionally, AI enhances fraud detection by flagging irregularities in real-time, bolstering financial security. As accounting firms adopt AI, professionals can focus on strategic tasks like advisory services and client relationships.
However, challenges like data privacy, integration costs, and the need for upskilling remain. Embracing AI in accounting promises a future of precision, scalability, and innovation, transforming traditional practices into dynamic, technology-driven solutions.
Table of Contents
- What Is AI Accounting?
- Can AI Replace Accountants?
- Benefits Of Artificial Intelligence In Accounting
- A.I. In Accounting Challenges
- How Is AI Used In Accounting?
- How To Get Started With Artificial Intelligence?
- AI Trends In Accounting 2025
- AI Tools Every Accountant Should Know About
- FAQ(Frequently Asked Questions)
- Final Takeaway
What Is AI Accounting?
AI accounting refers to the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies into accounting processes to automate, optimize, and enhance financial tasks. It leverages tools like machine learning, natural language processing, and robotic process automation to streamline activities such as bookkeeping, invoicing, expense tracking, payroll, and financial reporting.
AI systems analyze large datasets to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and predict financial trends, improving accuracy and efficiency. For example, AI can automate data entry, reconcile accounts, and flag potential fraud in real-time.
It also supports tax compliance and generates insights for better decision-making. By reducing manual work, AI allows accountants to focus on strategic roles like financial planning and client advisory. While offering benefits like cost savings and scalability, AI accounting raises challenges such as data security, implementation costs, and the need for professionals to adapt to new technologies.

Can AI Replace Accountants?
AI is unlikely to fully replace accountants but will significantly transform their roles. AI excels at automating repetitive tasks like data entry, bookkeeping, and transaction reconciliation, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Tools powered by machine learning can analyze vast datasets, detect anomalies, and generate financial insights faster than humans. For example, AI can automate tax calculations or flag potential fraud in real-time. AI in accounting is the future of accounting that no accountant can deny.
As per the Future of Jobs report, by 2030, the share of tasks carried out by individuals will decrease from 47% to 33%.
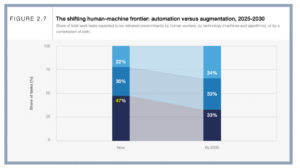
However, accountants provide critical judgment, strategic thinking, and client relationships that AI cannot replicate. Complex tasks like interpreting nuanced financial regulations, advising on business strategy, or navigating ethical dilemmas require human expertise.
AI may reduce demand for entry-level accounting roles focused on manual tasks, but it increases the need for accountants skilled in data analysis, AI tool management, and advisory services. Rather than replacement, AI empowers accountants to focus on higher-value work, provided they adapt to new technologies.
Benefits Of Artificial Intelligence In Accounting
There are several benefits of Artificial Intelligence that you must be well aware off. Some of the key factors that you must consider from your end.
1. Automation Of Repetitive Tasks
One of the most significant advantages of AI in accounting is its ability to automate repetitive, time-consuming tasks. Processes like data entry, invoice processing, and account reconciliation, which traditionally require hours of manual effort, can now be handled by AI-powered tools.
For example, software like Xero or QuickBooks, integrated with AI, can automatically categorize transactions, match invoices to payments, and update ledgers in real-time.
This automation eliminates the need for accountants to spend hours on mundane tasks, freeing them to focus on analysis and advisory roles. By reducing the time spent on routine work, AI enables firms to handle larger volumes of transactions without increasing staff, making it particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited resources.
2. Enhanced Accuracy & Reduced Errors
Human error is a persistent challenge in accounting, where even minor mistakes in calculations or data entry can lead to significant financial discrepancies. AI mitigates this risk by performing tasks with high precision.
Machine learning algorithms can process complex datasets, ensuring calculations for taxes, payroll, or financial statements are accurate. For instance, AI tools can cross-reference thousands of transactions against bank statements in seconds, flagging inconsistencies that might be overlooked by a human.
This accuracy is critical in maintaining compliance with financial regulations and avoiding costly penalties. Moreover, AI’s consistency ensures that repetitive tasks are performed uniformly, reducing the variability that can occur with human intervention.
3. Real-Time Fraud Detection & Risk Management
AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data in real-time makes it a powerful tool for detecting fraud and managing financial risks. Machine learning models can identify unusual patterns or anomalies in transactions, such as irregular payment amounts or suspicious vendor activity, that might indicate fraudulent behavior.
For example, AI systems used by firms like KPMG can flag discrepancies in expense reports or detect unauthorized transactions by comparing them against historical data and behavioral patterns.
This proactive approach enhances financial security and builds trust with clients. Additionally, AI can assess risks by analyzing market trends or client financial health, enabling accountants to provide early warnings about potential issues like cash flow shortages.
4. Predictive Insights For Strategic Planning
AI’s predictive capabilities are revolutionizing how accountants approach financial planning. By analyzing historical data and market trends, AI tools can forecast revenue, expenses, and cash flow with remarkable accuracy.
For instance, platforms like Sage use AI to predict future financial outcomes based on past performance, helping businesses plan budgets or investments. These insights enable accountants to move beyond retrospective reporting and offer proactive advice, such as identifying cost-saving opportunities or recommending investment strategies.
This shift transforms accountants into strategic partners, enhancing their value to clients and organizations. Predictive analytics also supports scenario planning, allowing businesses to model the financial impact of decisions like expanding operations or entering new markets.
5. Cost Efficiency & Resource Optimization
AI reduces operational costs by automating labor-intensive processes and minimizing the need for additional staff. For example, automating accounts payable and receivable processes can cut processing costs by up to 80%, according to some industry estimates.
Smaller firms benefit significantly, as AI enables them to compete with larger organizations without investing heavily in human resources.
Additionally, AI reduces the costs associated with errors, rework, and compliance penalties. By optimizing resource allocation, AI ensures that accounting firms can scale operations efficiently, handling increased workloads without proportional increases in expenses.

6. Scalability For Growing Business
As businesses grow, the volume and complexity of financial transactions increase exponentially. AI provides scalability by processing large datasets quickly and accurately, regardless of volume.
For example, an e-commerce company with thousands of daily transactions can rely on AI to manage inventory accounting, sales tax calculations, and financial reporting without delays.
This scalability is crucial for businesses operating in dynamic markets, where rapid growth demands robust financial systems. AI’s ability to handle complex tasks at scale ensures that accounting processes remain efficient and reliable, even as transaction volumes soar.
7. Improved Decision Making & Client Services
AI empowers accountants with actionable insights derived from data analysis, enabling better decision-making. By generating detailed reports and visualizations, AI tools help accountants communicate complex financial information to clients in an accessible way.
For instance, AI-driven dashboards can highlight key performance indicators (KPIs) like profit margins or liquidity ratios, enabling clients to make informed decisions. This capability strengthens client relationships, as accountants can offer tailored advice that aligns with business goals.
Furthermore, AI’s ability to process unstructured data, such as emails or contracts, using NLP allows accountants to extract relevant financial information quickly, enhancing responsiveness and service quality.
Few insightful articles on Accounts to improve your knowledge:
- Income From House Property: A Guide To The Tax Payer
- Top 30 Journal Entries Questions And Answers
- Can Science Students Become An Accountant?
- All You Need To Know About Audit Trail In Zoho Books
- What Is General Ledger Accounting And How Does It Work?
- Source Documents In Accounting: Overview, Usages & Types
A.I. In Accounting Challenges
Artificial Intelligence (AI) promises transformative benefits for accounting, but its adoption is not without significant hurdles. As of October 2025, recent reports like Karbon’s State of AI in Accounting Report 2025 and CPA.com’s 2025 AI in Accounting Report highlight persistent challenges that can impede progress, increase risks, and strain resources.
These issues span technical, ethical, human, and organizational domains, requiring strategic mitigation to realize AI’s full potential.
Below is a detailed exploration of the key challenges, drawing from 2025 industry insights, with practical examples and implications for accounting firms.
1. Data Privacy & Security Concerns
A top barrier, cited by 70% of professionals, is the risk of data breaches when AI processes sensitive financial information. AI tools often store data on third-party servers, raising fears of leaks or misuse for model training.
For instance, the 2017 Deloitte cyberattack compromised 244,000 records via cloud services, underscoring ongoing vulnerabilities.
In 2025, 23% of firms report security impacts stalling adoption in workflows like tax prep. This erodes client trust, invites fines under GDPR or SOX, and demands robust encryption and compliance checks.
2. Lack Of Training & Upskilling
Only 37% of firms invest in AI education, leaving 57% of teams untrained and prone to errors. Beginners save just 46 minutes daily versus 79 for experts, per Ace Cloud Hosting’s analysis.
The SHSCONF ICDDE 2025 paper notes rising skill barriers, with new entrants needing AI proficiency amid 50% potential job automation.
Without training, outputs go unvalidated, leading to compliance issues and resistance. CPA.com emphasizes a “mindset shift” for scaling, but gaps widen the divide between adopters and laggards.
3. Fear Of Job Displacement
28% of accountants fear redundancy, especially in bookkeeping (57% vulnerable). PwC’s RPA cut manual roles, per the SHSCONF study, projecting 50% displacement by 2045.
Karbon reports 20% concern in operations roles, fostering disengagement. While AI handles “boring” tasks like classification, it shifts jobs to analysis—but without reskilling, cultural fractures emerge, reducing morale.
4. High Cost Of Implementation
Upfront expenses for AI software, integration, and training deter SMEs. Expert Market notes AI apps cost more than traditional ones, with GE’s SAP integration delaying projects by six months and adding $5M.
Legacy upgrades amplify this, per CPA.com’s legacy vs. AI-native tension. Smaller firms face 6% yearly skepticism rise due to unaffordable infrastructure.
5. Integration With Legacy System
Incompatible tech stacks cause delays and errors. Traditional ERP like SAP struggles with AI’s real-time needs, leading to incomplete data processing.
The SHSCONF GE case exemplifies middleware costs and disruptions. Fragmented infrastructure affects mid-sized firms most, hindering scalability.
6. Ethical Issues
46% distrust AI due to bias risks, where historical data perpetuates inequalities in audits or lending. AI in Accounting can have ethical issues so while making the application of AI ensure that you follow the right path.
Paylocity highlights ethical governance needs; opacity (“black box”) complicates accountability. Fraud via generative AI, like fake invoices, adds misuse risks, demanding human oversight.
7. Loss Of Human Touch
47% worry AI diminishes client relationships, prioritizing efficiency over empathy. Karbon notes decreased interactions could harm satisfaction in advisory roles.
As AI automates routine work, firms risk commoditization without balancing personalization. AI In Accounting can assist you in reaching your goals with complete ease.
8. Transparency & Explainability
AI’s opacity hinders audits. The CPA Journal and Becker stress the need for verifiable outputs. Explainable AI tools are emerging fixes. The table below showcases the challenges of implementation of AI in accounting.
| Challenge | Impact Level | Mitigation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Data Privacy | High (70%) | Encryption & audits |
| Training Gaps | High (57%) | Role-specific programs |
| Job Displacement
Legacy Integration |
Medium (28%)
High |
Reskilling initiatives
Tech audits |
| Ethical Bias | Medium (46%) | Diverse datasets |
| Human Touch Loss | Medium (47%) | Hybrid models |
| Compliance | Medium | Regular audits |
| Leadership Gaps | Low-Medium (19%) | Open dialogues |
| Costs | High | Phased rollouts |
| Transparency | High | Explainable AI |
How Is AI Used In Accounting?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming accounting by automating tasks, enhancing accuracy, and enabling strategic insights. Using machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and robotic process automation (RPA), AI streamlines workflows and empowers accountants to focus on high-value roles. Below are the primary ways AI is applied in accounting, based on 2025 industry trends.
1. Automated Bookkeeping
AI tools like QuickBooks and Xero automate data entry and transaction categorization. Using OCR, they scan invoices and receipts, reducing manual work by 75%, per Ace Cloud Hosting. For example, Xero’s AI auto-matches 80% of bank transactions, saving hours daily.
2. Financial Reporting
AI generates real-time financial statements, such as balance sheets, with platforms like Sage Intacct. CPA.com notes 65% of firms use AI for reporting, improving compliance and accuracy by 20%. EY’s AI, for instance, produces audit-ready reports in seconds. AI in accounting can help you in proper report presentation.
3. Fraud Detection
ML algorithms detect anomalies in transactions, flagging potential fraud. KPMG’s AI tools identify irregular payments, cutting detection time by 60%, per the CPA Journal. A $200,000 embezzlement was caught via Paylocity’s AI analysis.
4. Tax Compliance
AI simplifies tax preparation by applying updated regulations. Tools like Avalara reduce errors by 50%, per TW Accounting, handling complex multi-jurisdictional filings efficiently. Karbon reports 30–40 hours saved per tax season. AI in accounting needs proper documentation and tax compliance to meet your goals.
5. Accounts Payable/ Receivable
RPA tools like Bill.com automate invoice processing and payment tracking, speeding up workflows by 80%. AI predicts payment delays, improving cash flow, as seen in Zoho Books’ 25% reduction in overdue receivables.
6. Predictive Forecasting
AI forecasts financial trends using historical data. NetSuite’s AI improves budgeting accuracy by 20–30%, per CPA.com, aiding strategic planning. A retailer avoided losses by adjusting costs based on Sage’s predictions.
7. Auditing
AI analyzes entire datasets for audits, not just samples. Deloitte’s tools cut audit time by 40%, though human oversight remains critical to avoid errors, per Becker.
How To Get Started With Artificial Intelligence?
There are some simple steps to get started with Artificial Intelligence. You must go through some of the simple steps to meet your goals with ease.
1. Assess Your Current Processes
Identify pain points like manual data entry, invoice reconciliation, or forecasting bottlenecks. Inventory existing tools and pinpoint automation opportunities for quick wins (e.g., repetitive tasks in AP/AR).
2. Build The Foundational Knowledge
Learn AI basics through free resources (see below). Experiment with simple tools like ChatGPT for tasks such as drafting emails or summarizing reports to understand its potential without overwhelm.
3. Develop An AI Strategy
Involve stakeholders (e.g., CPAs, IT leads) to set goals, timelines, and a roadmap. Align AI with business objectives, like improving client advisory services, and address resistance through feedback loops.
4. Select & Implement Tools
Choose AI-integrated software that fits your budget, scales with growth, and integrates with systems like ERP or cloud hosting (e.g., QuickBooks on Cloud). Start with cloud-based SaaS for low upfront costs.
5. Train Your Team
Mandate training on tools and ethical AI use. Make it ongoing to bridge skills gaps, reduce errors, and encourage daily integration (e.g., using AI for at least one task weekly).
6. Pilot & Scale
Test AI on low-risk areas (e.g., invoice processing) before expanding. Monitor performance, ensure data quality (clean inputs prevent errors), and evaluate ROI through metrics like time saved.
7. Ensure Security & Compliance
Use tools with robust protocols (e.g., SOC2 compliance) and establish governance for data privacy. Always oversee AI outputs with human review. AI In Accounting is that revolution that can change the life of the accountant forever.
AI Trends In Accounting 2025
As of October 2025, artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer an emerging technology in accounting—it’s a core driver reshaping workflows, decision-making, and professional roles. According to the AICPA and CPA.com’s 2025 AI in Accounting Report, 83% of accounting professionals are actively using AI, up significantly from prior years, with the global AI in accounting market valued at $6.68 billion this year and projected to reach $37.6 billion by 2030 at a 41% CAGR.
This growth reflects AI’s shift from basic automation to strategic augmentation, enabling accountants to focus on advisory services amid talent shortages and regulatory pressures.
Karbon’s State of AI in Accounting 2025 Report highlights that advanced AI users save 71% more time (79 minutes per task vs. 49 for beginners), while firms investing in AI training see 22% greater efficiency gains—equating to 40 hours saved annually per employee.
So Let’s Explore the current AI in Accounting trends to have a clear insight about the current market:-
1. Widespread Adoption For Generative AI For Work Flow Augmentation
Generative AI (GenAI), including tools like ChatGPT and domain-specific models, is transforming routine tasks into intelligent processes. In 2025, 69% of tax and accounting firms plan to bring more work in-house using GenAI for drafting documents, summarizing reports, and conducting research—up from 8% full adoption in 2024. Key applications include:
- Automated Reporting and Analytics: AI analyzes financial statements for anomalies, generates commentary on revenue/expense trends, and enables real-time dashboards. 97.2% of companies now invest in big data AI for trend identification and forecasting.
- Email and Correspondence: 25% of firms use GenAI for drafting, reducing manual effort by up to 30%. Intuit’s 2025 QuickBooks Accountant Technology Report notes that tech-forward firms using GenAI for these tasks report 17% median revenue growth from client advisory services (CAS). On X, professionals echo this, with one post highlighting GenAI’s role in boosting reporting detail and real-time forecasting.
2. Agentic AI And Predictive Analytics For Strategic Forecasting
Agentic AI—autonomous systems that plan and execute tasks like tax prep or audits—is gaining traction, shifting accountants toward advisory roles. By 2026, Gartner predicts 90% of finance teams will use at least one AI-powered solution for predictive analytics, flagging risks and forecasting cash flows with 82% greater accuracy than manual methods. Trends include:
- Fraud Detection and Anomaly Spotting: AI scans datasets for irregularities, reducing global fraud losses (estimated at $3.1 billion annually) through real-time alerts.
- Scenario Planning: Tools simulate economic shifts, aiding compliance with new 2025 standards like crypto asset disclosures and ESG reporting. Thomson Reuters’ Future of Professionals Report forecasts AI will handle 38% of CFO workloads in payables, receivables, and payroll, addressing the talent gap where 75% of CPAs are nearing retirement.
3. Integration Of AI With Blockchain And Cloud For Secure, Real Time Operation
Hybrid tech stacks combining AI, blockchain, and cloud computing are streamlining reconciliation and compliance. Blockchain’s immutable ledgers paired with AI enable continuous auditing, cutting month-end close times by 50% and ensuring GAAP/SOX adherence. Key shifts:
- Smart Contracts and Automation: Self-executing agreements automate invoicing and tax withholding, integrated with robotic process automation (RPA) for error-free IRS filings.
- Cloud-Based Systems: 81% of firms outsource to cloud platforms for real-time reporting and data security, emphasizing privacy amid rising cyber threats. X discussions highlight blockchain-AI synergies for fraud detection and decentralized data control, aligning with 2025’s focus on transparency.
4. AI Driven Talent Management & Upskilling
With an unemployment rate of just 2.0% for accountants and a projected decline in clerical roles (seventh-fastest per the World Economic Forum), AI is filling gaps by enabling firms to operate with 38% fewer staff in routine areas. Trends:
- Skills Prioritization: 75% of firms now emphasize AI/big data skills in hiring, with “AI and big data” as the fastest-growing competency through 2030.
- Training Investments: Only 25% of firms trained teams in 2024, but 2025 sees a surge, with AI addressing entry-level shortages. Intuit’s survey reveals firms blending AI with human oversight to enhance client experiences, projecting 99% CAS revenue growth.
5. Ethical AI, Regulation And Human In Top Loop Governance
As AI proliferates, 2025 emphasizes “human-in-the-loop” verification to mitigate risks like biases and errors. CPA.com identifies strategic themes including workflow automation balanced with ethical oversight, while new regulations target AI in audits and crypto reporting. Challenges:
- Data Privacy and Bias: 61% view AI as an opportunity but cite ethical hurdles; robust frameworks are essential.
- Regulatory Evolution: Expect standards for GenAI transparency in tax and ESG, with AI aiding compliance but requiring human review. X users stress ongoing learning to combat “AI anxiety,” positioning ethical adoption as a competitive edge.
AI Tools Every Accountant Should Know About
In 2025, AI tools are essential for accountants to automate routine tasks, enhance accuracy, and unlock strategic insights. Based on recent industry analyses, the following table highlights essential must-know tools, selected for their impact on key areas like invoicing, auditing, forecasting, and compliance.
| Tool Name | Key Features | Best For | Pricing (as of 2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vic.ai | AI-driven invoice processing, anomaly detection, auto-matching to POs, and real-time approvals with 99% accuracy. Integrates with QuickBooks, Sage, and Xero. | Accounts Payable (AP) automation and fraud prevention. | Starts at $1,500/month for small teams; enterprise custom. |
| Zeni | Automated bookkeeping, expense categorization, real-time dashboards, and predictive cash flow forecasting. Combines AI with human oversight. | Startups and small firms needing end-to-end financial ops. | $549/month base; scales with transactions. |
| Netgain | Flux analysis, automated reconciliations, asset management, and month-end close acceleration. Embeds in ERP like NetSuite. | Financial reporting and reconciliation workflows. | $2,000+/month; per-user licensing. |
| Docyt | OCR for receipt/invoice extraction, automated bookkeeping, and compliance checks. Learns from historical data for smarter categorization. | Expense management and document-heavy tasks. | $99/user/month; free trial available. |
| Botkeeper | Full AI bookkeeping suite with transaction categorization, payroll integration, and custom reporting. Scales for multi-entity firms. | Mid-sized firms outsourcing routine bookkeeping. | Custom; starts around $500/client/month. |
FAQ(Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are the main applications of AI in accounting?
AI is primarily used for automating data entry, invoice processing, transaction reconciliation, and fraud detection through machine learning algorithms that analyze patterns and reduce errors. It also supports predictive analytics for cash flow forecasting, financial reporting, and audit efficiency, while tools like generative AI draft memos or emails, saving significant time—up to 71% more for advanced users compared to beginners.
2. Will AI replace accountants and bookkeeping jobs?
No, AI is not poised to replace accountants; instead, it augments their roles by handling repetitive “boring” tasks like transaction classification and back-office processing, freeing professionals for higher-value work such as client advisory and decision-making. Studies show AI users support more clients, close books 7.5 days faster, and report higher job satisfaction, with only 1 in 10 firms fully integrating it yet, emphasizing human oversight for ethics and complexity.
3. What are the benefits of using AI in accounting?
Key benefits include increased efficiency (e.g., unlocking seven weeks of capacity per employee annually in AI-adopting firms), improved accuracy in compliance and fraud detection by minimizing false positives, cost savings through automation, and better work-life balance. AI also enhances strategic insights via data analysis, boosting productivity by 8.5% on routine tasks and enabling faster, higher-quality reporting.
4. What are the challenges or risks of implementing AI in accounting?
Challenges include data privacy concerns, potential inaccuracies in interpreting complex regulations (e.g., tax laws), and the need for training to avoid over-reliance—49% of firms have no plans due to caution. Additional risks involve high initial costs for tools like ChatGPT ($20–$25/month) and the learning curve for transitioning platforms, requiring a “human-in-the-loop” approach to ensure ethical use and error correction.
5. How can accounting firms get started with AI tools?
Start by assessing needs and selecting user-friendly tools like AI-powered software for AP/AR automation (e.g., BILL or Xero) or generative AI like ChatGPT for drafting. Invest in employee training—firms with AI education save 22% more time per employee—and begin with low-risk tasks like email composition (used by 64% of accountants). Pilot integrations with existing ERPs, monitor for security, and scale based on ROI, such as reducing memo creation from four hours to 30 minutes.
Final Takeaway
Hence, these are some of the crucial facts about AI in accounting that can assist you in getting the maximum returns from your learning. As in this digital age you need to stay updated to get the job done within a shorter version of time.
Share your views and opinions in our comment box. This will assist us to know your take on this matter. Once you follow the correct process, things will become easier for you in the long run.
- 3 Smart Ways to Speed Up Data Entry and Processing in Excel - January 27, 2026
- How to Convert Images Containing Tables into Editable Excel - January 27, 2026
- One Nation, One ID: Understanding the Academic Bank of Credits - January 22, 2026